Understanding Cologne Perfume
Cologne perfume, often referred to as “eau de cologne” (EDC), is a lighter form of fragrance compared to traditional perfume. The main difference lies in the concentration of aromatic compounds. While perfume can have a fragrance concentration of 15 – 40%, eau de cologne typically contains only 2 – 5% of these compounds. This results in a more subtle and less intense scent that evaporates more quickly.
There is a common misconception that cologne is exclusively a male fragrance. In modern times, the lines between men’s and women’s fragrances have blurred significantly. Many perfume houses now offer gender – neutral or unisex colognes, catering to a broader audience that values scent over traditional gender norms.
The History of Cologne
The Origin of Cologne
Cologne has its roots in 1709 in Cologne, Germany. Giovanni Maria Farina, an Italian perfumer, created the original cologne, which he named after his new hometown. He aimed to capture the essence of an Italian spring morning, combining vibrant citrus and delicate floral notes. The fragrance was designed to evoke the freshness and vitality of blooming flowers and the zest of citrus fruits, creating a harmonious blend that became instantly popular. Farina’s cologne quickly gained acclaim for its unique composition and refreshing aroma, establishing it as a timeless classic in the world of perfumery.
The Evolution of Cologne
Initially, cologne was used as a medicinal tonic, believed to possess antiseptic and refreshing properties. It was also thought to ward off diseases, making it a valuable addition to personal hygiene routines. Over time, cologne evolved into a luxury fragrance, gaining popularity for its ability to enhance one’s personal allure. As its appeal expanded, cologne became a status symbol, with both men and women incorporating it into their daily lives to project sophistication and charm. The transition from medicinal use to a fashionable accessory underscores the evolving cultural significance of cologne, reflecting broader shifts in societal values and aesthetics.
Cultural Impact
4711 Cologne is an iconic example of the cultural impact of cologne. First produced in 1792, it is one of the oldest and most well-known colognes in the world. The brand’s longevity and enduring popularity can be attributed to its unique blend of citrus and aromatic notes, which has remained consistent over centuries. It has become a symbol of German heritage and is still popular today, representing the classic style of eau de cologne. The name ‘4711’ originates from the address of the original pharmacy in Cologne where it was first sold, adding a layer of historical significance to its legacy. Over time, 4711 Cologne has been embraced by various generations, becoming a staple in many households and a favorite among fragrance enthusiasts. Its distinctive green bottle design, introduced in the early 20th century, further solidifies its status as a timeless icon in the world of perfumery.
Key Ingredients in Cologne Perfumes
Classic Citrus Base
The classic cologne scent is characterized by a citrus base, often featuring bergamot, lemon, and orange. These citrus notes provide a fresh, invigorating, and uplifting aroma, making cologne a popular choice for daytime wear. The bright and zesty scents can awaken the senses and leave a feeling of cleanliness.
Herbaceous Accents
Lavender, rosemary, and neroli are common herbaceous ingredients in cologne. These herbs add a more complex and sophisticated layer to the fragrance. Lavender brings a calming and floral element, while rosemary adds a slightly spicy and earthy note. Neroli, derived from orange blossoms, gives a sweet and delicate floral touch.
Modern Variations
To appeal to a wider audience, especially in the context of unisex fragrances, modern colognes often include wood and musk notes. Wood notes like sandalwood and cedarwood provide a warm, grounding effect, while musk adds a soft, sensual undertone.
Cologne vs. Perfume: Concentration & Use Cases
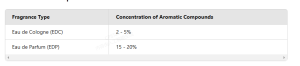
This difference in concentration means that EDP has a stronger and longer – lasting scent compared to EDC.
Application Scenarios
Eau de cologne is ideal for daytime use. Its light and fresh scent won’t be overpowering in casual settings, such as work, running errands, or outdoor activities. Eau de parfum, on the other hand, is better suited for evening events, formal occasions, or when you want a more intense and long – lasting fragrance.
Gender – Neutral Usage Trends
As mentioned earlier, the modern trend is towards gender – neutral fragrances. Both men and women are now equally likely to choose cologne based on personal preference rather than traditional gender – specific scents.
How to Choose & Apply Cologne
Pulse Point Application
The best places to apply cologne are the pulse points, such as the wrists and the sides of the neck. The heat from these areas helps to diffuse the fragrance more effectively. When applying, gently spray or dab a small amount on these points. Avoid rubbing the wrists together, as this can break down the fragrance molecules and alter the scent.
Layering Tips
To enhance the longevity and complexity of the fragrance, you can layer cologne with complementary products. For example, use a scented body lotion or shower gel with similar notes before applying the cologne. This creates a more cohesive and long – lasting scent experience.
Storage Recommendations
To preserve the integrity of your cologne, store it in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and heat. Extreme temperatures can cause the fragrance to break down and lose its original scent. Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use.
FAQ Section
Is cologne only for men?
No, cologne is not only for men. In the past, it was often associated with male fragrances, but modern trends have led to the creation of many gender – neutral and unisex colognes. Both men and women can enjoy and wear cologne based on their personal scent preferences.
How long does cologne last compared to perfume?
Cologne generally lasts for a shorter period compared to perfume. Due to its lower concentration of aromatic compounds (2 – 5% in cologne vs. 15 – 40% in perfume), cologne may need to be reapplied more frequently. A cologne scent can last anywhere from 2 – 4 hours, while perfume can last 6 – 8 hours or even longer.
Can cologne be used as aftershave?
Yes, cologne can be used as an aftershave. Its light and refreshing properties can soothe the skin after shaving and leave a pleasant scent. However, make sure the cologne does not contain any ingredients that may irritate freshly shaved skin. Some people prefer to use a dedicated aftershave balm or lotion first and then apply cologne for a combined effect of skin care and fragrance.
Leave a Reply